eLearning Diagnostic Tool Proposal: Accessible Design - School Refusal
A concept for Education Research. This tool is designed for students, educators, caregivers and administrators to identify strategies to encourage truant kids back into classrooms.
Designed by Amanda Marsh, August 2025
Context
Secondary College X has a significant truancy (or school refusal) problem.
Truancy presents in three distinct ways:
a) non attendance all day, consistently
b) selective non attendance (seeking a ‘safe space’ on campus)
c) selective non attendance (roaming and interfering with other classes on campus)
School refusal at Secondary College X is most commonly seen among ASD and indigenous students.
Concept
A diagnostic tool that seeks information from the school refusers, caregivers and staff to identify:
a) causes of school refusal
b) push factors
c) pull factors
(Totsika, V., Hastings, R. P., Dutton, Y., Worsley, A., Melvin, G., Gray, K., Tonge, B., & Heyne, D. (2020)
Resulting information can be used to diagnose key problems and identify solutions between all stakeholders to build resilience in students and improve school attendance.
Pedagogy
Students in this cohort form two types:
a) standard or above academic norm with poor social skills.
b) low academic due to a history of sporadic school attendance.
Due to part of the cohort being from category b, the tool will use language appropriate for a NAPLAN Proficiency result of Needs Additional Support at a Year 7 level. (ACARA 2025)
All levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy will be utilised. Some qualitative questions may require higher order thinking, while quantitative questions will use lower levels. It will primarily pivot between Level 2: Understanding, and Level 3: Applying. It can however, where appropriate, offer a pictorial or symbolic way to present options that reflect up to Level 6: Creating, by asking students to imagine perfect school-based and home-based learning spaces. (Monash University 2025)
As the user converses with the chat bot, the bot will identify students with higher literacy band levels and converse at a level appropriate to them, but only in circumstances that do not distort data collection.
Significant portions of the tool will be dependent on visuals minimising literacy and numeracy challenges.
Users will be able to have any text read to them by the tool itself.
The tool will be designed in such a way that it switches between aural, written and image based interactivity periodically to allow for ‘brain breaks’ - a key need of many students who would be surveyed by this tool.
Multimodel
This tool will fall into the category of qualiquantative research data. (Totsika, V., Hastings, R. P., Dutton, Y., Worsley, A., Melvin, G., Gray, K., Tonge, B., & Heyne, D. (2020).
Central to this tool will be a combination of interactive image making, chat bots, ranking systems and prompts to collect information that is based on sentimental analysis in the style of cultural probes.
Quantitative data will be collected from all stakeholders in reference to truancy frequency, location, time, motivations and excuses.
Qualitative data will be generated by asking conversing about truant behaviour patterns, consequences, triggers and solutions.
The Tool will begin all conversations by ascertaining whether the user is a student, teacher, administrator or caregiver. This will direct the Tool to pursue particular lines of enqiry.
Example Content - Quantative Data
Example Content - Qualitative Data
How many days a week do you go to school?
How many days a week do you go but leave early or arrive late?
When you avoid a lesson, where do you go?
Is there a subject you regularly do attend?
If you avoid a class, is it because of the learning content, noise, other students, teacher, location, time of day or time of month?
Using the shapes and symbols shown here, create a map of a classroom environment you find overwhelming or stressful.
Using just one single continuous line, draw how a stressful class feels for you.
Now create another line drawing that shows what a welcoming classroom looks or feels like.
Using the Adobe colour scheme generator, create a colour set that represents how you feel when you need to avoid a lesson or class.*
Privacy & Security
All data will be encrypted and a secure environment maintained.
Individual identities will need to be collected but will only be made available to very specific people who can make change. These people will be referred to at the beginning of the process so that all individuals understand that the process is designed specifically to assist in meeting their individual learning and psychological safety needs.
Example Users
Annika 16 year old girl with ASD. Chronic school avoider. Two parent home. Both parents are highly educated. Mother has similar ASD traits. Mother is overprotective and allows her to stay home.
Mahtiel 12 year old boy, Nyoongar. Lives with mum but has a regular rotation of aunties, uncles, cousins and grandparents (kinship relationships) who stay for weeks at a time. Lives in social housing with little money or resources. Will have some issues operating computer software and will require assistance to complete. Attends school daily but roams the yard continuously. Avoids eye contact with teachers and struggles to communicate effectively with authority figures. Gets on well with AIEOs. Often leans on them heavily for support and/or to avoid consequences of poor behaviour.
Rebecca Single parent of 14 year old boy. Boy refuses to enter most classes, seeking Student Services support as a ‘safe space’ instead. Student is undiagnosed. Mother cannot afford to get an official diagnosis and the wait time is lengthy. She is frustrated and time poor with little support of her own.
Colin Teacher of Humanities. Has a huge range of abilities and behaviours in their year 9 class. Several students rarely turn up, slowing down the learning of others as significant teaching time is taken up catching these kids up one on one when they do attend. Literacy in many students is below the national average. The challenges of the class are compounded by disruptive behaviours and the constant use of mobile phones in class. Two students have been withdrawn from school for swearing at and threatening him recently, though their absence has barely impacted the stress levels he experiences every time he teaches this class.
Annette Ambitious Senior Administrator (Deputy) at a medium cost Catholic school wants to implement new programs to improve school attendance and outcomes for school/class refusers. School has a slightly above average literacy/numeracy rate relative the State average and a 33/33/33% Anglo-Australian, Afro-Australian and Indian-Australian cultural mix. She is convinced that their NAPLAN and WACE scores could be increased. She wants to achieve this while also improving cost efficiencies and staff stress levels in the Pastoral Care team.
Accessibility
Future
Resources
Chat GTP
Voiceflow
Adobe CS
Articulate 360
TouchDesigner
Other(TBC)
As per the Pedagogy statement (above), the entire tool will be operating in language that is comprehendable to users with the lowest of literacy levels. It will be aural and voice activated where appropriate.
Images and text will be of a scale suitable for users with vision impairment.
Because this is targeted at students with psychological stress, it will use positive reinforcement and reassurance throughout. (Catania 1984)
For those with information processing issues such as ADD, ADHD, dsylexia or dyspraxia, it will be designed to also provide ‘brain breaks’ switching between different types of activities including suggestions of physical movement. (Flanagan, Nathan-Roberts 2019)
*Qualitative Question sample
Using the colour generator, choose a set of colours that best reflect how you feel when you are in your ‘safe space’.
You can move the group around, move one colour up or down or use the Custom option in the Dropdown Box.
Ethics
Cultural sensitivities must be considered at all phases of development. Communication in an indigenous context is complex and a long game. Trust must established before any indigenous community member is likely to consider using this tool.
Essential to development is co-designing with local communities. In this case, Nyoongar community elders, parents, AIEOs and supporting organisations such as Clontarf, Follow The Dream, Deadly Sista Girlz and others.
Cultural sensitivities must be considered at all phases of development. Communication in an indigenous context is complex and a long game. Trust must established before any indigenous community member is likely to consider using this tool.
Essential to development is co-designing with local communities. In this case, Nyoongar community elders, parents, AIEOs and supporting organisations such as Clontarf, Follow The Dream, Deadly Sista Girlz and others.
After initial design testing and implementation, this tool will be further developed to incorporate student, school and community co-design capabilities.
By integrating TouchDesigner, a student could get weekly animated colour ‘experiences’ that take their cue from actual attendance data and the colour and line diagrams they generated during the qualitative Q&A session - a sort of phenomenological attendance chart. As a form of gamefication, students are encouraged to change the colour palette generated from week to week. (Petch 2025)
References
Adobe. (n.d.). Adobe Color. https://color.adobe.com/create/color-wheel
Articulate Global, LLC. (2025). Articulate 360 https://www.articulate.com/360/://ww.articulate.com/360/ttps://www.articulate.com/360/
Australian Government. (2024, April). Australian Government response to the Senate Standing Committees on Education and Employment report: The national trend of school refusal and related matters.
Baxter, L., & Meyers, N. (2021). Learning from high-attending urban Indigenous students: A case study. The Australian Journal of Indigenous Education, 50(2), 348–358. https://doi.org/10.1017/jie.2020.6
Canva. (n.d.). Canva. https://www.canva.com/
Catania, A. C. (1984). The operant behaviorism of B. F. Skinner. The Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 7(3), 473–475.
Clark, S. (2023, April 19). School refusal (Research Paper Series, 2022–23). Social Policy Section, Parliament of Australia, Department of Parliamentary Services, Parliamentary Library.
Collard, L. M. (2009). Djidi Djidi, Wardong, Kulbardi, Walitj and Weitj: Nyungar Dream Time messengers.
Contreras-Ortiz, M. S., Puello Marrugo, P., & Rodríguez Ribón, J. C. (2023). E-learning ecosystems for people with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3277819
Derivative. (n.d.). Touch Designer: Derivative. https://derivative.ca/
Dream Design Collective. (2024). Dream Design Collective agreement 2024 Wurundjeri Biik, VIC. National Indigenous Youth Education Coalition (NIYEC).
Flanagan, J., & Nathan-Roberts, D. (2019). Theories of vigilance and the prospect of cognitive restoration. Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting, 63(1). https://doi.org/10.1177/1071181319631506
Monash University. (n.d.). Align with taxonomies. In Teach HQ. Retrieved [Date], from Monash University website. NAP
Meyers, C. A., & Bagnall, R. G. (2015). A case study of an adult learner with ASD and ADHD in an undergraduate online learning environment. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 31(2), 208–220.
National Assessment Program. (n.d.). Results and reports. Australian Curriculum, Assessment and Reporting Authority. Retrieved [Date], from NAP website. NAP
National Indigenous Youth Education Coalition. (2024, March 21). The school exclusion project research report.
Parliament of Australia. (2023). The national trend of school refusal and related matters: Submission 127, Senate Inquiry into School Refusal / School Can’t. Education and Employment References Committee. Australian Parliament HousePursuit
Petch, N. (2025). [Slide deck]. Victoria University.
Saggers, B., Mavropoulou, S., Carrington, S., Paynter, J., Adams, D., Malone, S., Westerveld, M., McKeown, G., Constantine, C., Bartlett, T., B., C., Gately, J., Heath, S., Porter, A., Stewart, C. J., Winspear-Schillings, H., Nepal, S., Dunne, J., Saggers, A., Wilde, J., van Leent, L., Wright, N., Marsh, C., & O’Connor, K. (2023, April). Removing educational barriers in Australian schools for autistic students: Current trends, gaps, and recommendations for educational research, inclusive policy, and educational practice (White Paper). Autism CRC.
Squarespace. (n.d.). Squarespace. https://squarespace.com/
Totsika, V., Hastings, R. P., Dutton, Y., Worsley, A., Melvin, G., Gray, K., Tonge, B., & Heyne, D. (2020). Types and correlates of school nonattendance in students with autism spectrum disorders. Autism, 24(7), 1639–1649. https://doi.org/10.1177/1362361320916967
Voiceflow. (n.d.). Voiceflow. https://www.voiceflow.com/
Adobe 2025
Application in the real world
This tool is designed to be a diagnostic tool that can be used in any school context anywhere in the world.
By using interactive game, learning tech and AI, it taps into student interests while collecting information usable at a micro or macro level in the education system to improve the social and academic outcomes of school refusers.
By encouraging education staff on the front line, support workers and carers to add input as well, a picture can be drawn that reveals where support systems get it ‘right’ or ‘wrong’ and where student input can improve what is already happening. Based on the data collected, changes could be made at single school campus or at a state system level.
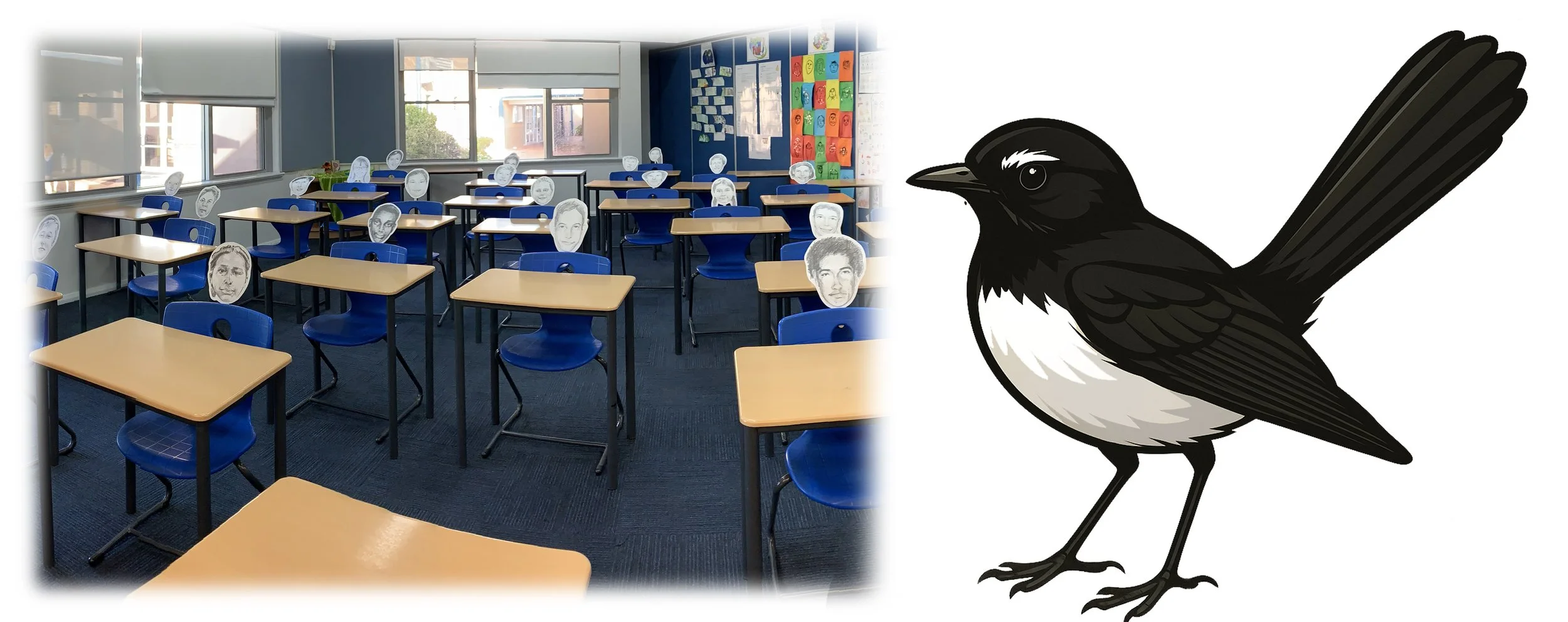
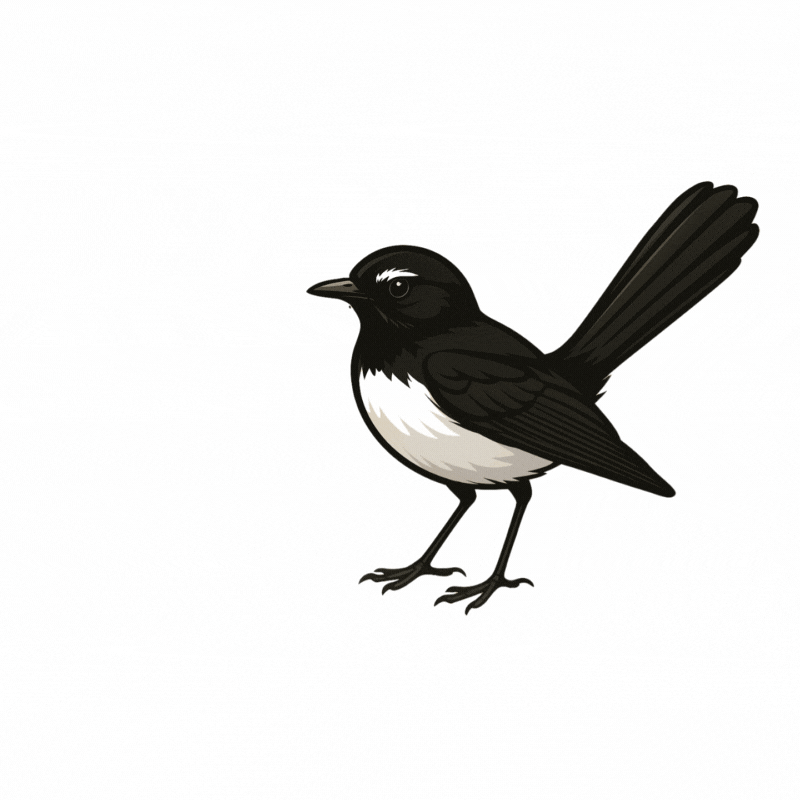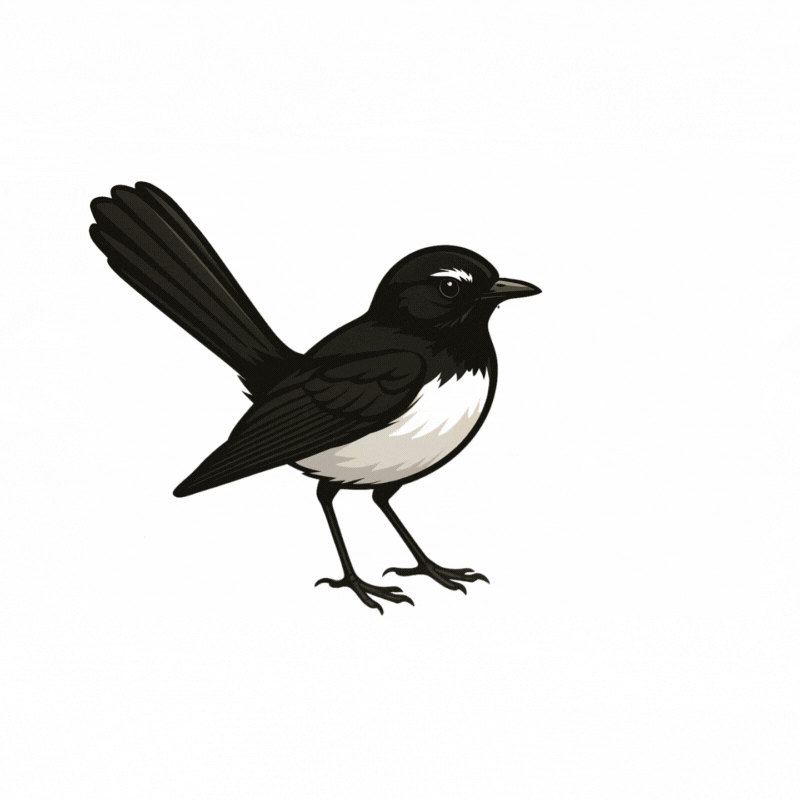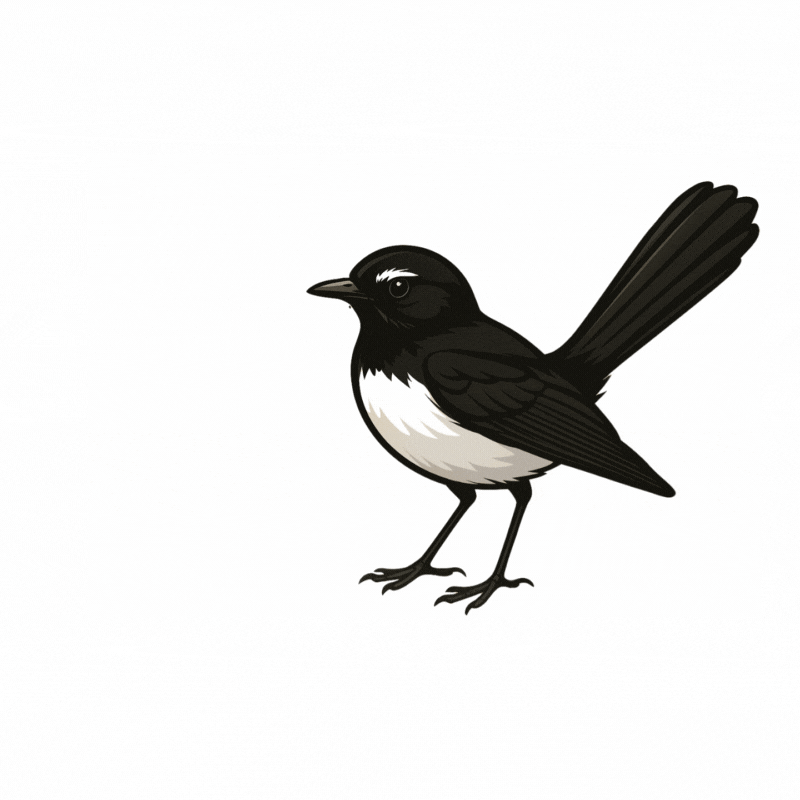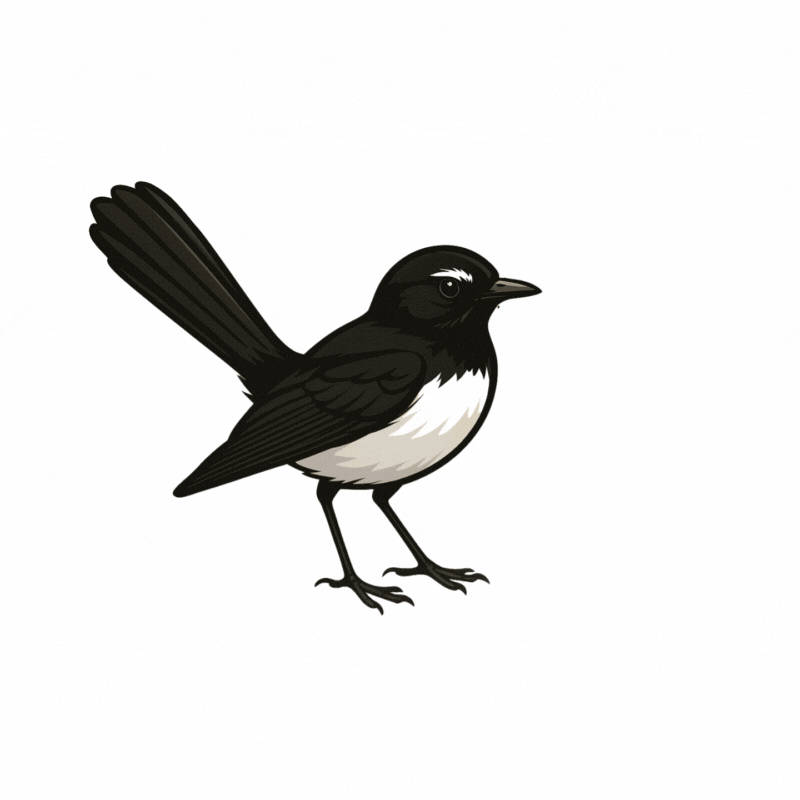
Chatbot avatar
Djiti djiti bird.
Symbolic messenger and protector.
Common across Australia. Suitable to both Aboriginal and non-Aboriginal students, staff and communities. (Collard 2009)
Brain break example
Make the djiti djiti bird dance.
Users can earn points for the complexity, speed and degree of ‘flitting about’ the djiti djiti does. Points can also be gained for collecting bugs, harrassing crows and other commonly seen actions of the bird.
Chatbot Backstory
Djiti Djiti has ADHD. They are very active and never stop talking! Djiti Djiti can annoy bigger people and/or adults. They are highly effective at what matters to them. Djiti Djiti loves communicating and is definitely an extravert.